Introduction
A method of establishing control points, their position being determined by measuring the distances between the traverse stations (which serve as control point) and the angles subtended at the various stations by their adjacent stations.
Principles of Theodolite
The principles of the theodolite
are that a beam of light travels in a straight line, and that when you
know the length of one side of a triangle and the angles of the corners
as measured by reflecting beams of light then you can precisely map
features on the ground both horizontally and vertically.
Type of Theodolite
Figure 1 : Type of Theodolite
Theodolite Vernier
The
vernier theodolite is a also know as a transit. In a transit theodolite
or simply transit the telescope can be rotated in a vertical plane.
Earlier versions of theodolite were of the non-transit type and are
obsolete now.
Two
view of a vernier theodolite are in Figure 2. The instrument details
vary with different manufacturers but the essential parts remain the
same.
Figure 2 : Component of Theodolite Vernier
Theodolite Optic
Theodolite Optic is a precision direction type of instrument for observing horizontal and vertical directions. In an optical theodolite, the horizontal and vertical dials are made of optical glass and the optical system of the horizontal and vertical dial microscope transmits images of diametrically opposite end lines of the dials to the field of the reading microscope.
Figure 3 : Component of Theodolite Optic
Figure 4 : Circle-reading optical system of Theodolite Optic
Figure 5 : How to reading of Theodolite Optic
Digital Theodolite
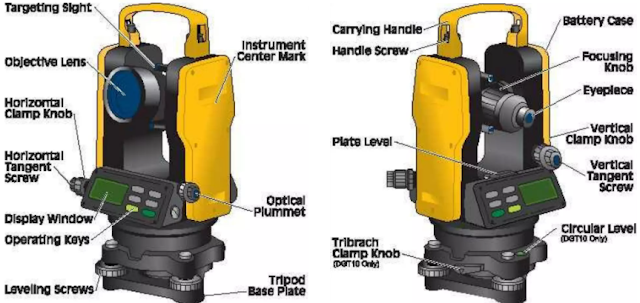
A digital theodolite consists of a telescope mounted on a base, as well as an electronic readout screen used to display horizontal and vertical angles. A digital theodolite is convenient because the digital reading replaces the traditional graduated circle, and this produces a more accurate reading.
Figure 6 : Component of Digital Theodolite
Total Station
Figure 7 : Basic Concept of Total Station
Figure 8 : Component of Total Station